Animal Nutrition
About Department
Established in 1966, this Department is doing pioneer work in fundamental as well as applied animal nutrition. In addition to under-graduate and post-graduate teaching, guidance is given to Master’s and Doctoral degree students. The Department caters to the need of livestock and poultry farmers by providing advisory services, testing of feed quality and supplying quality mineral mixture. This Department has fully equipped laboratories, classrooms, and facilities for conducting nutritional research on cattle, buffalo, sheep, goat and poultry, and all the necessary state of the art/latest equipment and infrastructural facilities for estimation of various nutritional parameters, well qualified faculty and skilled manpower for imparting training and conducting need based research.
Formulation of balanced and economic feeds and feeding of various classes of animals is an important area of interest of the Department. There exists a modern facility for storing of feeds and fodder, feed plant for preparation of compounded feed and mineral mixture to meet the requirement of various user Departments of the University.
In teaching through need based periodical revision it has built a broad based postgraduate program covering basic and applied nutrition of cattle, buffalo, small ruminants, poultry, fish and wild/Zoo animals. It also offers courses on clinical animal nutrition and feed technology. The Department is having robust facility for analysis of feed and fodder samples. Samples of feeds and fodders from the Remount Veterinary Corps, various state Government agencies, Feed factories and different laboratories and farmers are analysed to ascertain the quality of feed and fodder.
Head of the Department :
Dr. Sajjan Sihag
Phone (O): 01662-256118
E-mail: hod.ann@luvas.edu.in
Formulation of balanced and economic feeds and feeding of various classes of animals is an important area of interest of the Department. There exists a modern facility for storing of feeds and fodder, feed plant for preparation of compounded feed and mineral mixture to meet the requirement of various user Departments of the University.
In teaching through need based periodical revision it has built a broad based postgraduate program covering basic and applied nutrition of cattle, buffalo, small ruminants, poultry, fish and wild/Zoo animals. It also offers courses on clinical animal nutrition and feed technology. The Department is having robust facility for analysis of feed and fodder samples. Samples of feeds and fodders from the Remount Veterinary Corps, various state Government agencies, Feed factories and different laboratories and farmers are analysed to ascertain the quality of feed and fodder.
Head of the Department :

Dr. Sajjan Sihag
Phone (O): 01662-256118
E-mail: hod.ann@luvas.edu.in
Research and Teaching
Non- Teaching Staff (AN)
| Dr. Sajjan Sihag | Principal Scientist and Head | View Details |
| Dr. B. S. Tewatia | Principal Scientist | View Details |
| Dr. V. S. Panwar | Principal Scientist | View Details |
| Dr. Zile Singh Sihag | Principal Scientist | View Details |
| Dr. Raj Singh | Professor | View Details |
| Dr. N.S. Maan | Principal Scientist | View Details |
| Dr. Nancy Sheoran | Assistant Professor | View Details |
| Dr. Sushil Kumar | Scientist | View Details |
| Dr. Jyotsana | Assistant Professor | View Details |
Non- Teaching Staff (AN)
| Sh. Karambir Singh | Assistant |
| Sh. Mahabir Parsad | Lab. Technician |
| Sh. Anand Parkash | Lab Technician |
| Sh. Deepak Kumar | Lab Technician |
| Sh. Shalinder | Clerk |
| Sh. Vinay Kumar | Clerk |
| Krishan Kumar Rohilla | Mechanic |
| Satyawan | Lab Assistant |
| Sh. Parmod Kumar | Messenger |
| Munsi Ram | Animal Attendent |
| Satwanti | Animal Attendent |
| Bhanti Devi | Beldar |
| Sh. Balwan Singh | Agriculture Inspector |
| Sh. Mahavir Singh | WPO |
| Sh. Yogesh | Beldar |
| Sh. Parbhu Dayal | Beldar |
| Sh. Sunil Kumar | Beldar |
| Sh. Kartik Sharma | Beldar |
 Nutritional survey in sixteen districts of Haryana viz. Sirsa, Fatehbad, Hisar, Bhiwani, Rohtak, Jhajjar, Mohindergarh, Rewari, Gurgaon, Faridabad, Panipat, Kurukshetra, Kaithal, Ambala, Sonepat and Yamunanagar has been completed to assess the mineral status of feeds, fodders and animals. A common observation in all the districts was that none of the farmers is supplementing mineral mixture in routine except for therapeutic purpose and only about 20-25 % farmers are feeding common salt. In general, higher Ca deficiency was recorded during lean period whereas during green period, P deficiency was more. Further, widespread deficiency of Zn was recorded in almost all the districts besides varying deficiency levels of Mn and Cu.
Nutritional survey in sixteen districts of Haryana viz. Sirsa, Fatehbad, Hisar, Bhiwani, Rohtak, Jhajjar, Mohindergarh, Rewari, Gurgaon, Faridabad, Panipat, Kurukshetra, Kaithal, Ambala, Sonepat and Yamunanagar has been completed to assess the mineral status of feeds, fodders and animals. A common observation in all the districts was that none of the farmers is supplementing mineral mixture in routine except for therapeutic purpose and only about 20-25 % farmers are feeding common salt. In general, higher Ca deficiency was recorded during lean period whereas during green period, P deficiency was more. Further, widespread deficiency of Zn was recorded in almost all the districts besides varying deficiency levels of Mn and Cu.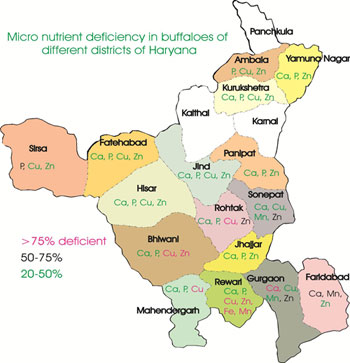 Facilities have been created for manufacturing of mineral mixture. Quality mineral mixture for cattle, buffalo and poultry is being prepared and made available to farmers and user departments at reasonable prices.
Facilities have been created for manufacturing of mineral mixture. Quality mineral mixture for cattle, buffalo and poultry is being prepared and made available to farmers and user departments at reasonable prices.Popularization of the mineral mixture among the farmers of the State is being done by conducting trainings, delivering lectures, interactions and conducting field studies.
Supplementation of linseed oil and Ca salt of linseed oil @ 2% of DMI in Sahiwal cattle enhanced the total CLA content of milk fat by 182.9 and 44.7%, respectively. It also increased the level of MUFA and PUFA in the milk fat.
Inclusion of linseed (whole/ground) in the concentrate mixture of cows resulted in reduction of cholesterol by 49.9% and 33.9% in whole and ground linseed, respectively and increased the CLA content of milk fat.
 The growth and reproductive performance of the crossbred calves / heifers will enhance if fed 15% higher level of energy and protein over the NRC standard.
The growth and reproductive performance of the crossbred calves / heifers will enhance if fed 15% higher level of energy and protein over the NRC standard.Nutritive value of stover of HHB-67 (improved) genotypes of bajra was superior to HC-20 and HHB-197 genotypes.
The high yielding buffaloes particularly those yielding more than 18 litres /day are unable to meet their nutrient needs from the feeding practices followed by farmers of Hisar district.
The forages could be economically evaluated for their nutritional qualities through modified chemical techniques by reducing the cost of detergents/chemicals by 2/3, ¾ and ½ of those in original methods for NDF, ADF and its fractionation besides crude protein, respectively.
 Groundnut cake, mustard cake and barley should be ground through 5 mm sieve for concentrate mixture of calves to save energy/electricity consumption and better performance of calves.
Groundnut cake, mustard cake and barley should be ground through 5 mm sieve for concentrate mixture of calves to save energy/electricity consumption and better performance of calves.Nutritional evaluation of Berseem variety HFB-600, proved to be superior than the commonly grown variety HFB 130 or the check variety Mascavi.
The Beetal kids grow faster when supplemented with both energy and protein sources in addition to grazing.
Chemical composition and IVDMD of foliage from different seed sources of Prosopis Juliflora vary considerably. Prosopis Juliflora lopping can serve as a rich source of protein in the dietary regimen of small ruminants.
Among the leaf samples of Prospis cineraria, P. cineraria hybrid and P. chinensis, P cineraria hybrid with 31.85% crude protein and 72.4% IVDMD was rated the best species for animal feeding. Lopping of different species of Prosopis can successfully maintain non lactating goats without any adverse effect on the nutrient intake and digestibility.
 Murrah buffalo calves fed total mixed ration (TMR) based on mustard cake and sunflower cake resulted in body weight gain of 700 g/day. The cost of providing one kg DCP as well as TDN to the heifers was lowest in animals fed this TMR. Feeding cost of this ration for one kg body weight gain was recorded as Rs.15.36.
Murrah buffalo calves fed total mixed ration (TMR) based on mustard cake and sunflower cake resulted in body weight gain of 700 g/day. The cost of providing one kg DCP as well as TDN to the heifers was lowest in animals fed this TMR. Feeding cost of this ration for one kg body weight gain was recorded as Rs.15.36.On farm trials were conducted at farmers’ fields. The feeding practices followed by the farmers were compared with those developed based on total mixed rations. Feeding cost per kg milk production was reduced by 25 per cent by feeding total mixed rations.
De-oiled sunflower cake can be used as an economical alternate source of protein instead of groundnut cake replacing 50-100% of protein of groundnut cake in lactating cattle and buffalo without affecting nutrient utilization, milk yield and other milk parameters.
An insight of the feeding systems of lactating buffaloes of Hisar district revealed feeding of 27% extra protein to 12-15 Kg. yielders; 9.5% deficient TDN to 15-18 kg yielders while deficiency of 18%protein and 29% TDN in > 18 kg yielders.
Higher growth rate in buffaloes and higher birth weight of new born calves was observed in buffaloes fed higher energy during last two month of gestation. Milk yield was also higher at higher energy level; Cost of milk production reduced in buffaloes fed pre-paratum 30% higher energy.
Mustard cake can safely replace groundnut cake without affecting rumen fermentation pattern, nutrient digestibility and protein bound iodine in cattle and buffalo.
Safe and economical replacement of 50% of groundnut cake with extracted sunflower cake for growing buffalo calves is recommended.
Phulsi, a moong crop residue mixture consisting of broken and small size grains, empty pods and straw can be incorporated up to a level of 60% in the concentrate mixture of kids and lambs.
 The Broccoli was found to contain 23.96% DCP and 87.20% TDN. The dry matter intake of Broccoli was 2.67% of body wt. in goats indicating its high nutritive value and palatability.
The Broccoli was found to contain 23.96% DCP and 87.20% TDN. The dry matter intake of Broccoli was 2.67% of body wt. in goats indicating its high nutritive value and palatability.Lactating goats fed Broccoli fodder based ration performed better in terms of milk yield and its composition than those fed Berseem fodder based ration.
It is not economical to raise Munjal lambs at higher level of nutrition than the prescribed ICAR feeding standards.
Densified complete feed blocks containing straw, concentrate, molasses, mineral mixture binder and water were prepared using block making machine developed by the department.
 The manufacturing techno logy of multi-nutrient supplement of urea-molasses-mineral block lick in a solidified form was developed.
The manufacturing techno logy of multi-nutrient supplement of urea-molasses-mineral block lick in a solidified form was developed.A technique for making berseem hay without loss of leaves has been developed.
The Beetal goat when supplemented with 25% higher energy + 25% higher protein than the prescribed ICAR standard resulted in higher body weight gain in kids & higher milk production in lactating goats.
To attain a body weight of 20 kg for male and 15 kg for female Beetal kids at 6 months of age, supplementation of crushed maize @ 1/100th of body wt. is beneficial and economical.
Munjal lambs have higher growth potential than cross-bred lambs and supplementation of maize along with eight hours of grazing resulted in economic returns in both the breeds.
The groundnut cake can be completely replaced by cheaper sources of protein like guar meal, mustard cake, and cotton seed cake in the supplementary concentrate mixtures without affecting the growth rate, feed efficiency, wool yield and meat quality in Nali Lambs reared under stall fed conditions.
Supplementation of wheat or barley grain along with eight hours of grazing improved the growth performance of lambs.
Feeding of reconstituted bajra grain to lambs is economical as compared to raw bajra
The activity of various rumen enzymes was higher in solid rumen contents fraction followed by extra cellular and cellular fraction. The cellulolytic enzyme activities were higher in animals fed low roughage ration. The activity of proteases was higher in animals fed high roughage ration.
Dietary sulphur up to 0.24 % of dry matter resulted in higher ruminal protein nitrogen concentration, microbial population and microbial enzyme activities. Sulphur supplementation of the high fibrous diets improved the fiber utilization by ruminants.
Studies conducted on rumen ecosystem of cattle and buffalo revealed that buffalo had better rumen ecosystem for utilization of low grade roughages. Isolation and characterization of rumen bacteria, protozoa and fungi was also done.
The mixing time of 10 minutes was recommended for homogeneity of feed in horizontal mixer which gave optimum performance in broilers.
Phytase supplementation to low P maize and wheat based diets improved feed intake, body weight gain and feed efficiency.
Maize can be successfully replaced up to a level of 66% by pearl millet without affecting growth, feed efficiency, performance index, carcass traits and muscle composition.
Barley as energy source can be safely used at 25% level in broiler diet replacing not more than 25% of maize with multi enzyme supplementation.
Replacement of 50% maize with pearl millet without multi enzyme and at 100% level with multi enzyme in broiler ration is economical.
A diet having particle size 905µ GMD, 9% crude fiber supplemented with multi enzyme economizes broiler production.
 Better pellet durability and hardness was observed in treatments using hydrated lime and a combination of molasses plus hydrated lime as binders.
Better pellet durability and hardness was observed in treatments using hydrated lime and a combination of molasses plus hydrated lime as binders.Broiler production was more profitable when 50% maize was replaced with pearl millet and it was not profitable when 20% soybean was replaced with sunflower meal.
Groundnut cake can be replaced up to 30% by mustard cake treated with 3g Cu2SO4/Kg. mustard cake without affecting growth, feed efficiency, carcass traits and economics of broiler production.
The rations containing mustard cake and guar meal were deficient in sulphur. The addition of inorganic sulphur to deficient rations improved the performance of broilers.
The addition of enzyme to diets containing ground pearl millet improved the body weight gain and feed efficiency in broilers.
For earning more profit from poultry farming, heated pearl millet ground through 2 mm sieve size can be incorporated in place of maize at 100 % level in the ration of broilers.
Post graduate students/ Research assistants/ Senior research fellows
Gunjan, M.V.Sc. student
Parul Rana, M.V.Sc. student
Rohit Kumar, M.V.Sc. student
Rohit, M.V.Sc. student
Shubhnish Bisla, M.V.Sc. student
Rahul Singh Chandal, M.V.Sc. student
Mukesh Sihag, M.V.Sc. student
Pardeep Kumar, M.V.Sc. student
Ravinder, M.V.Sc. student
Meetu, M.V.Sc. student
Ritu, M.V.Sc. student
Ph.D. Students
1. Vinus
2. Shubham Thakur
3. Sandeep Kumar
4. Ramswroop
5. Vivek Saharan
6. Sunil Dev Singh
7. Anuj Singh
Ongoing projects
- Nutritional studies in livestock and poultry
- Economic quality feed manufacturing for ruminants and poultry
- Amelioration of mineral deficiency in livestock of Haryana state
- Quality feed manufacturing for different livestock and poultry species maintained at animal farm of the university (Self Financing Scheme)
- Sustainable Rice Straw Management Through Improving its Feed Value for Ruminants (RKVY Project)





